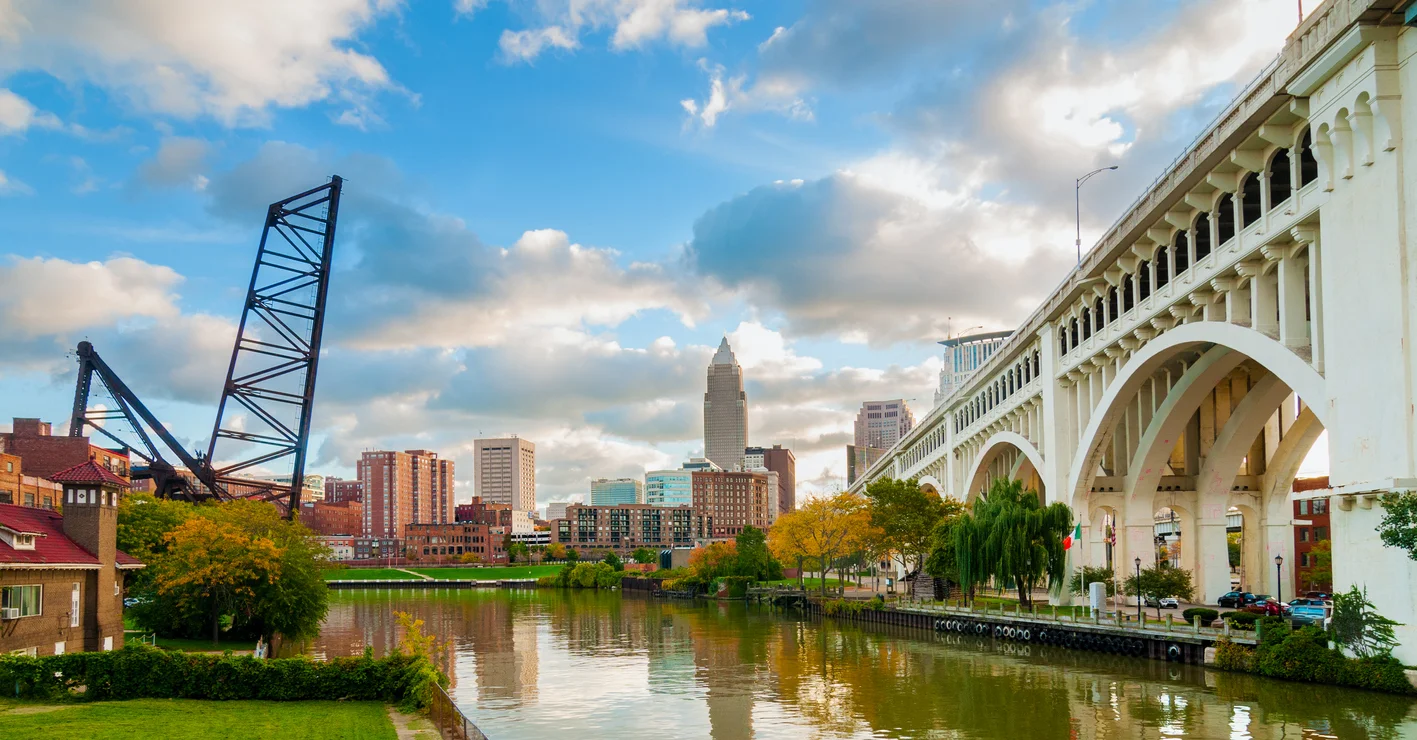
By Jacob Wolf, Research Associate Combined sewer overflows (CSO) stink—both environmentally and economically—for Ohio’s cities. In many urban areas built up in the 19th and early 20th centuries, stormwater runoff drains into the same pipes that carry raw sewage to treatment facilities. Most days, all of the combined sewer and storm water makes it safely to the treatment plants. However, when there is heavy rainfall, the systems overload, and the excess untreated water gets diverted into rivers and lakes. This is referred to as a CSO event. Cincinnati, Cleveland, Columbus, and other cities around Ohio and the rest of the country are under mandates from the United States E.P.A. to reduce or eliminate the amount of CSO discharged into their waterways.
The strategies the affected cities are developing to reduce their CSO can be broadly categorized as either “gray infrastructure” or “green infrastructure.” “Gray” refers to building new pipes and tunnels underground to hold the excess water. “Green” involves using plants, gardens, and open space on the surface to reduce the amount of storm water runoff that gets into the pipes in the first place. The Plain Dealer recently ran a series of articles that analyzed the pros and cons of both approaches, focusing on the Northeast Ohio Regional Sewer District (NEORSD)’s $3 billion project to build new underground tunnels.
Green infrastructure has many benefits for urban revitalization. It commonly appears as street-side landscaping features or open, undeveloped space. It can also mean “daylighting” previously covered streams and waterways. Some green infrastructure projects transform vacant or abandoned property into “rain gardens.” All these forms of green infrastructure have great aesthetic benefits that improve the quality of urban places as they capture storm water and keep it out of the sewers.
The City of Philadelphia is leading the charge for green solutions to the CSO problem. Philadelphia’s 25-year, $2.4 billion CSO reduction plan will spend roughly 70% of the program’s budget on 8,000 to 12,000 acres of green projects. Officials estimate that this will eliminate about 8 billion gallons of sewage overflow per year. By contrast, the NEORSD tunnel project devotes only 2.5% of its $3 billion budget to green infrastructure.
However, NEORSD leaders and other critics argue that green methods alone will not prevent enough overflow events. Even if Philadelphia’s plan succeeds, it will still produce more gallons of overflow than Northeast Ohio does now. Furthermore, Philadelphia is not under an EPA consent decree, so it does not have the same stringent benchmarks to meet that NEORSD and other Ohio districts have.
Reducing and eliminating CSO discharge is key for economic development in legacy cities. Cleaner waterways create more desirable places that people want to live, work, and play. As it performs its utilitarian function of mitigating stormwater runoff, green infrastructure beautifies neighborhoods and creates vibrant, new public spaces. It can increase property values and provide a tool for disposing of vacant and abandoned residential property. Even if green infrastructure isn’t the only solution for CSOs, it should be at least be part of the solution due to the additional benefits it provides.